Space Optimization Strategies for 700 sq ft Houses: House Design For 700 Square Feet
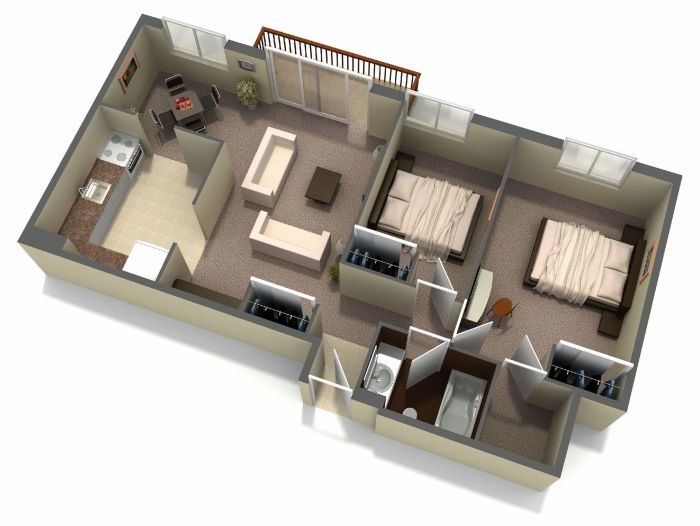

House design for 700 square feet – Optimizing space in a 700 sq ft home requires careful planning and the strategic use of furniture and design elements. Maximizing vertical space, employing multi-functional pieces, and clever storage solutions are key to creating a comfortable and functional living environment within a smaller footprint. This section will explore several effective strategies for achieving this.
Floor Plan Design with Built-in Furniture
A well-designed floor plan is crucial for maximizing space in a small home. Built-in furniture, such as custom-designed shelving units, window seats with storage, and Murphy beds, can significantly increase usable space by eliminating the need for freestanding pieces. For example, a built-in banquette seating area in the kitchen or dining area can provide seating while simultaneously incorporating storage underneath.
Similarly, a built-in bookshelf that stretches from floor to ceiling can replace multiple freestanding bookshelves, freeing up valuable floor space. Consider using a space-saving design that includes a walk-in closet or utilizes the space under the stairs for extra storage.
Space-Saving Furniture Solutions
Several furniture solutions are specifically designed to minimize their footprint. Sofa beds, for instance, offer seating during the day and convert into a bed at night, eliminating the need for a separate guest room. Ottomans with storage provide seating and extra storage space for blankets, pillows, or other items. Nesting tables can be easily stored away when not needed, and stackable chairs are ideal for smaller dining areas.
Vertical storage solutions, such as tall and narrow bookshelves or wardrobes, maximize vertical space without encroaching on valuable floor area. Consider a wall-mounted desk that folds away when not in use.
Multi-Functional Furniture Design Ideas
Multi-functional furniture is essential for small spaces. A coffee table with drawers or a lift-top can provide extra storage or a workspace. Beds with built-in drawers underneath offer valuable storage for clothing or bedding. A daybed with storage underneath can serve as a sofa during the day and a bed at night. Modular furniture, which can be easily reconfigured to suit different needs, is also an excellent option.
Imagine a sofa that converts into a sleeping space and has storage underneath – a truly space-saving marvel.
Comparative Table of Space-Saving Techniques
| Technique | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Built-in Furniture | Custom-designed furniture integrated into the architecture. | Maximizes space, often aesthetically pleasing, customisable to your needs. | Can be expensive, difficult to remove or modify later. |
| Multi-functional Furniture | Furniture with multiple uses (e.g., sofa bed, ottoman with storage). | Saves space, versatile, cost-effective compared to buying multiple pieces. | May compromise functionality of each individual use, could look less stylish than dedicated furniture. |
| Vertical Storage | Utilizing wall space for shelving, cabinets, and other storage solutions. | Maximizes vertical space, keeps floor space clear, efficient storage. | Can be difficult to access upper shelves, requires careful planning. |
| Folding Furniture | Furniture that folds away when not in use (e.g., folding chairs, Murphy beds). | Saves space, easy to store, ideal for small rooms. | Can be cumbersome to fold and unfold, may not be as durable as traditional furniture. |
Kitchen and Bathroom Design in Compact Spaces
Designing a functional and aesthetically pleasing kitchen and bathroom within the confines of a 700 sq ft house requires careful planning and strategic use of space. Optimizing every inch is key to creating a comfortable and efficient living environment. This section explores practical design solutions for compact kitchens and bathrooms, focusing on layout, storage, fixtures, and design styles.
Compact Kitchen Layout
A galley kitchen, given its linear design, is often the most efficient choice for a small space. A well-designed galley kitchen, approximately 8ft x 5ft (40 sq ft), can accommodate all necessary appliances and counter space. One wall could feature a continuous countertop with a built-in sink and a range or cooktop, while the opposite wall houses cabinetry for storage and possibly a refrigerator.
A small island, if space permits, could provide extra counter space and seating. Consider using a pull-out pantry for maximum storage efficiency in a limited space. The use of light colors on walls and cabinets will help to create a sense of spaciousness.
Efficient Storage Solutions for Small Kitchens and Bathrooms
Maximizing storage is crucial in compact spaces. For kitchens, consider vertical storage solutions like tall cabinets reaching the ceiling, pull-out drawers for easy access to pots and pans, and corner units with rotating shelves. Under-sink organizers and slim-line spice racks help to utilize otherwise wasted space. In the bathroom, floating vanities offer storage while keeping the floor space open and airy.
Recessed shelving within shower walls can hold toiletries, and over-the-toilet storage units add significant storage without compromising floor space. Multi-functional furniture, such as a storage bench with a built-in hamper, is also beneficial.
Space-Saving Bathroom Fixtures and Layouts
Space-saving fixtures are essential for small bathrooms. A wall-mounted toilet frees up floor space and makes cleaning easier. A corner sink maximizes space utilization and provides a clean aesthetic. A walk-in shower, replacing a bathtub, opens up the space significantly, and choosing a smaller shower head and low-profile shower tray further enhances the effect. A smaller, more efficient bathroom exhaust fan helps to reduce moisture build-up, preventing mold and mildew and ensuring the space is always comfortable.
Consider using a shower door instead of a shower curtain to save space and improve the look.
Designing a comfortable home within 700 square feet necessitates clever space planning. Expanding your search to consider layouts offering slightly more space can provide valuable insights. For example, exploring options like those detailed in this helpful guide on house design in 900 square feet can inform your 700 sq ft design, highlighting efficient use of space and multi-functional furniture choices that translate well to smaller areas.
Design Styles for Small Kitchens and Bathrooms
Minimalist and Scandinavian design styles are particularly well-suited to small kitchens and bathrooms. These styles emphasize clean lines, simple shapes, and light, neutral colors, creating an illusion of spaciousness. A minimalist kitchen might feature handleless cabinets and integrated appliances, while a Scandinavian bathroom could incorporate natural materials like wood and stone, along with plenty of white space. Contemporary styles can also be successfully implemented in small spaces, using sleek, modern fixtures and fittings.
The key is to maintain a sense of order and avoid clutter. A consistent color palette throughout the room can enhance the sense of space.
Building Materials and Cost Considerations
Building a 700 sq ft house requires careful consideration of building materials to balance cost and quality. The choices made significantly impact the overall budget, influencing both initial investment and long-term maintenance expenses. Selecting cost-effective materials without sacrificing durability and energy efficiency is crucial for responsible home construction.The cost of building materials varies widely depending on location, availability, and quality.
Understanding these variations and planning a detailed budget is essential to avoid cost overruns. This section details the cost breakdown of common building materials and provides strategies for creating a realistic budget for a 700 sq ft home.
Cost-Effective Building Material Choices
Choosing cost-effective building materials doesn’t necessarily mean compromising on quality. Many affordable options offer excellent performance and durability when selected and implemented correctly. For example, using engineered lumber instead of solid lumber can significantly reduce costs without sacrificing structural integrity. Similarly, opting for fiber cement siding over traditional wood siding can provide superior weather resistance and longevity at a competitive price point.
Careful consideration of material sourcing and bulk purchasing can also generate substantial savings.
Building Material Cost Breakdown
The following provides a general cost breakdown for various building materials. Note that these figures are estimates and can vary significantly based on location, supplier, and quantity purchased. These figures represent per-unit costs and do not include labor or installation expenses.
- Foundation: Concrete (approx. $10-$15 per sq ft) – Costs vary depending on soil conditions and foundation type.
- Framing Lumber: Engineered lumber (approx. $5-$10 per linear foot) – This is a cost-effective alternative to solid lumber.
- Exterior Walls: Fiber cement siding (approx. $2-$5 per sq ft) – Offers superior durability compared to wood siding.
- Roofing: Asphalt shingles (approx. $1-$3 per sq ft) – A relatively inexpensive and widely available option.
- Interior Walls: Drywall (approx. $1-$2 per sq ft) – A standard and affordable option for interior wall construction.
- Insulation: Fiberglass batt insulation (approx. $0.50-$1.50 per sq ft) – Provides adequate thermal insulation at a reasonable cost.
- Windows and Doors: Vinyl windows (approx. $200-$500 per window) – Vinyl windows are a cost-effective alternative to wood or aluminum.
Creating a Realistic Budget
Creating a realistic budget for a 700 sq ft house involves meticulous planning and detailed cost estimation. It is advisable to start with a comprehensive list of all necessary materials and labor costs. Consider using online budgeting tools or consulting with a contractor to refine your estimates. Adding a contingency buffer (typically 10-20% of the total estimated cost) is crucial to account for unforeseen expenses.
For example, a projected budget of $100,000 should include a contingency of $10,000-$20,000 to accommodate unexpected issues or price fluctuations. Regularly monitoring expenses against the budget is also critical for effective cost management throughout the construction process. Breaking down the budget into phases (foundation, framing, roofing, etc.) allows for better tracking and management of individual cost components.
Exterior Design and Landscaping for Small Properties
Maximizing curb appeal and functionality in a small 700 sq ft house requires careful consideration of exterior design and landscaping. A well-planned approach can create a visually stunning and welcoming home, even within limited space. This section explores strategies for achieving this, focusing on visual appeal, low-maintenance solutions, and sustainable material choices.
Visually Appealing Exterior Design for a 700 sq ft House
A visually appealing exterior for a small house hinges on creating a sense of proportion and balance. Avoid overwhelming the structure with overly large features. Consider using a cohesive color palette – perhaps a light, neutral color for the main structure accented with darker trim around windows and doors to create visual interest. Well-placed architectural details, such as carefully chosen window boxes or a charming porch, can significantly enhance the overall aesthetic.
The style should complement the surrounding neighborhood, but with individual touches to ensure it stands out in a positive way. For example, a simple craftsman style with natural wood accents could be both charming and visually impactful on a smaller footprint. Clean lines and a well-maintained facade are key elements.
Creating Curb Appeal on a Small Lot, House design for 700 square feet
Curb appeal is crucial for a small property. Strategic landscaping plays a significant role. Instead of sprawling lawns, consider using vertical gardening techniques like climbing plants on trellises or walls. This maximizes space and adds visual interest. A well-defined pathway leading to the entrance creates a welcoming feel.
Adding strategically placed lighting, perhaps low-voltage path lighting or uplighting for architectural features, can dramatically improve the nighttime appearance. Even small details, such as a neatly painted front door or attractive house numbers, contribute significantly to the overall impression. Consider a small, well-maintained garden bed with colorful, low-growing plants near the entrance to add a pop of color.
Low-Maintenance Landscaping Options for Small Properties
Low-maintenance landscaping is essential for small properties to minimize upkeep time and effort. Xeriscaping, a landscaping approach that emphasizes water conservation, is particularly well-suited to small lots. This involves using drought-tolerant plants native to the region, requiring less watering and maintenance. Gravel pathways and patios reduce the need for mowing and weeding. Artificial turf is another option, eliminating the need for watering, mowing, and fertilizing, although it has environmental considerations that should be weighed.
Choosing hardy, low-growing shrubs and perennials further reduces maintenance demands. For example, a combination of lavender, rosemary, and sedum creates a visually appealing and low-maintenance border.
Exterior Design Incorporating Sustainable Materials
Sustainable materials significantly contribute to both the environmental impact and the aesthetic appeal of a small home. Recycled wood can be used for siding or decking, adding character and reducing the environmental footprint. Locally sourced stone or brick offers durability and a natural aesthetic. Consider using solar panels integrated into the roof design, not only generating clean energy but also adding a modern, sleek element to the exterior.
The use of low-emissivity (Low-E) windows reduces energy loss and contributes to a more sustainable design. For example, a house with reclaimed wood siding, a metal roof for durability and reflectivity, and strategically placed solar panels can represent a stylish and environmentally conscious design. Choosing paints with low VOCs (volatile organic compounds) further minimizes environmental impact.
Common Queries
What are some common mistakes to avoid when designing a 700 sq ft house?
Overcrowding the space with furniture, neglecting natural light, using dark colors, and failing to plan storage adequately are common pitfalls.
How can I make a small kitchen feel larger?
Light-colored cabinets, efficient lighting, and maximizing vertical space with shelving can create the illusion of more space.
What are some cost-effective building materials for a small house?
Consider engineered wood, vinyl flooring, and readily available local materials to reduce costs without sacrificing quality.
Are there any specific zoning regulations I should consider for a 700 sq ft house?
Zoning regulations vary by location. Check with your local authorities for specific requirements regarding lot size, setbacks, and building height restrictions before beginning your project.
